Abstract
这里记录一些关于攻击预测的研究和我阅读时的笔记,基本都是AI辅助阅读的,理解或者是专有名词上有错误还请指正。
这里以记录为主,一些我认为从技术角度上有用的论文会单独发精读的文章,特指那些公开了源码、数据集,或者有可能复现的文章(实际上我就是在找这样的文章,而这也是我记录的目的,我必须时刻提醒自己这一点,避免陷入一些无意义的调研工作)。
而就目前的情况看,这一领域没有公开源码的习惯,让我无处follow。所以我的工作可能还要持续一些时间,与此同时可能会关注一些和检测相关的工作——在Research of AttackDetect中记录。
在这里列一个目录表,方便查阅:
| 题目 | 单位 | 年份 | 来源 | 数据集 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cyber-Attack Prediction Based on Network Intrusion Detection Systems for Alert Correlation Techniques: A Survey | School of Computing, Faculty of Engineering, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia (UTM) | 2021 | Sensors: Advances in Secure Massive MIMO Systems | \ | 综述类文章,告警预测 |
| 基于网络防御知识图谱的0day攻击路径预测方法 | 信息工程大学 | 2022 | 网络与信息安全学报 | 自建 | 路径排序算法,路径预测 |
| CyberSecurity Attack Prediction: A Deep Learning Approach | Institut Supérieur des Sciences Appliquées et de Technologie de Sousse, University of Sousse, Tunisia | 2020 | 13th International Conference on Security of Information and Networks (SIN 2020) | Defcon提供的Ctf’17 | 深度学习,攻击类别 |
| Predictive Methods in Cyber Defense: Current Experience and Research Challenges | Institute of Computer Science, Masaryk University, Czech Republic | 2021 | Future Generation Computer Systems | SABU | 三个方法和任务 |
| Predictive Cyber Situational Awareness and Personalized Blacklisting: A Sequential Rule Mining Approach | Institute of Computer Science, Masaryk University, Czech Republic | 2020 | Future Generation Computer Systems | SABU | 关联规则,预测攻击类别 |
| ProAPT: Projection of APT Threats with Deep Reinforcement Learning | Tarbiat Modares University, Tehran, Iran | 2022 | COMPUTERS & SECURITY | DAPT2020 | 强化学习+深度学习,预测攻击类别 |
| Survey of Attack Projection, Prediction, and Forecasting in Cyber Security | Institute of Computer Science, Masaryk University | 2019 | IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials | \ | 综述类文章,攻击预测 |
| A Data Mining Approach to Generating Network Attack Graph for Intrusion Prediction | Computer Science Department, Huazhong University of Science and Technology | 2007 | International Conference on Fuzzy Systems and Knowledge Discovery (FSKD) | DARPA2000 | 关联规则,攻击图生成 |
| Using Attack Graphs for Correlating, Hypothesizing, and Predicting Intrusion Alerts | Center for Secure Information Systems, George Mason University, Fairfax | 2006 | Computer Communications | DARPA2000 | 攻击图生成 |
Content
Cyber-Attack Prediction Based on Network Intrusion Detection Systems for Alert Correlation Techniques: A Survey
Year: 2021, Authors: School of Computing, Faculty of Engineering, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia (UTM)
Abstract:
Advanced cyber attacks consist of multiple stages aimed at being stealthy and elusive. Such attack patterns leave their footprints spatio-temporally dispersed across many different logs in victim machines. However, existing log-mining intrusion analysis systems typically target only a single type of log to discover evidence of an attack and therefore fail to exploit fundamental inter-log connections. The output of such single-log analysis can hardly reveal the complete attack story for complex, multi-stage attacks. Additionally, some existing approaches require heavyweight system instrumentation, which makes them impractical to deploy in real production environments. To address these problems, we present HERCULE, an automated multi-stage log-based intrusion analysis system. Inspired by graph analytics research in social network analysis, we model multi-stage intrusion analysis as a community discovery problem. HERCULE builds multi-dimensional weighted graphs by correlating log entries across multiple lightweight logs that are readily available on commodity systems. From these, HERCULE discovers any “attack communities” embedded within the graphs. Our evaluation with 15 well known APT attack families demonstrates that HERCULE can reconstruct attack behaviors from a spectrum of cyber attacks that involve multiple stages with high accuracy and low false positive rates.
Record:
综述类文章,主要回顾了基于NIDS入侵警报的最新网络攻击预测、其模型及限制。下表比较好的说明了文章的主要内容:
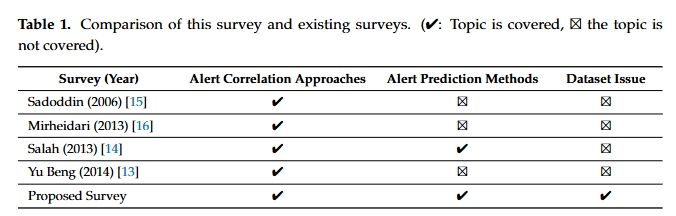
意思是,这些综述里就我们做了数据集的研究。
- 有关预测:
NIDS technology plays an essential role in protecting communication networks from cybercrime. However, these technologies are not viable in predicting future attacks. It produces much of alerts when attack activities/intrusions have effectively occurred. A proactive approach is to predict and lead conceivable attacks to prevent damage. However, network intrusion prediction is still an active investigation.
大意是检测不行了,预测更牛,但是也更难;那么预测到底有哪些方法?
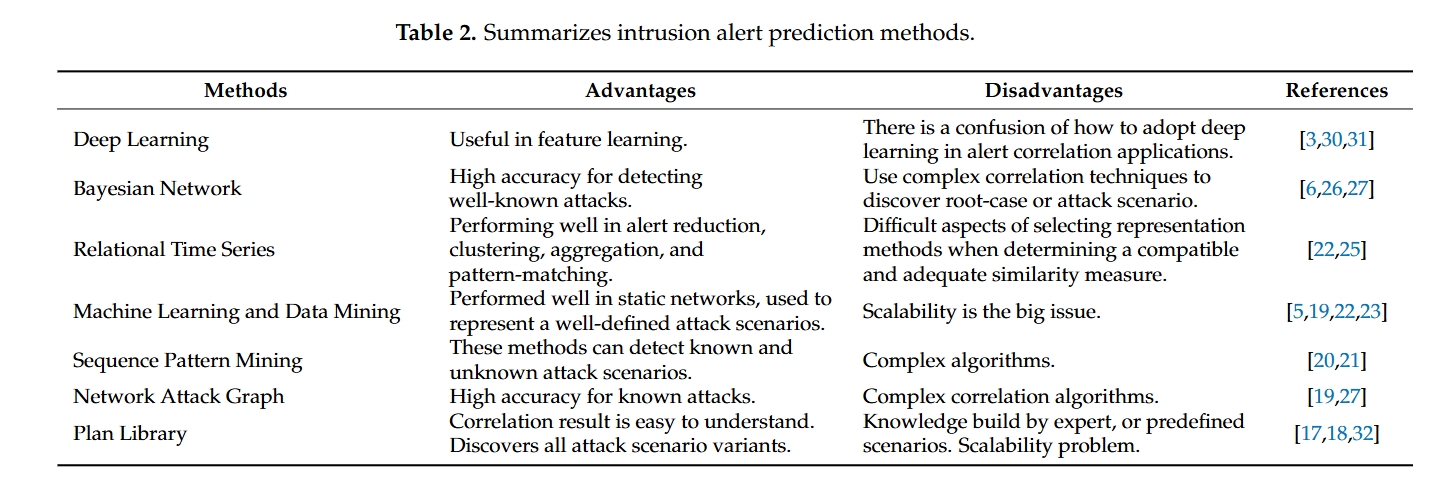
简单汉化一下:
| 方法 | 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|
| 深度学习 | 在特征学习中很有用 | 警报关联如何应用 |
| 贝叶斯网络 | 检测知名攻击的准确性高 | |
| 关系时间序列 | 在告警减少、聚类、聚合和模式匹配方面表现良好 | |
| 机器学习和数据挖掘 | 在静态网络中表现良好,用于表示明确定义的攻击场景 | |
| 序列模式挖掘 | 这些方法能够检测已知和未知的攻击场景 | |
| 网络攻击图 | 在已知攻击的高准确率 | |
| 计划库 | 关联结果易理解,能够发现所有攻击场景的变体 |
相关工作单独列出来,写在表里有些难看:
深度学习:
Shallow and Deep Learning Approaches for Network Intrusion Alert Prediction
GRU-based deep learning approach for network intrusion alert prediction
Network entity characterization and attack prediction
贝叶斯网络:
A Model-Based System for Intrusion Detection Using Novel Technique-Hidden Markov Bayesian
in Wireless Sensor Network
A Bayesian network-based approach for learning attack strategies from intrusion alerts
Multi-step Attack Scenarios Mining Based on Neural Network and Bayesian Network Attack Graph
关系时间序列:
机器学习和数据挖掘:
序列模式挖掘:
网络攻击图:
Attack scenario reconstruction approach using attack graph and alert data mining
Multi-step Attack Scenarios Mining Based on Neural Network and Bayesian Network Attack Graph
计划库:
目前看下来,比较有效和接近设想的可能是深度学习、贝叶斯网络、网络攻击图三种方法。
- 有关告警:
大量低质量警报是一个主要问题,需要进行告警关联;现有的方法有:
1、基于相似性的方法主要关注于提升警报属性的质量问题。
2、基于统计的方法则致力于通过警报之间的统计或因果关系来识别攻击场景。
3、基于知识的方法则通过预定义的重要性来处理攻击定义。
此外,基于混合的方法能够综合利用这三种关联方法的优势。
(具体的内容感觉和预测没关系,不作记录)
- 有关关联告警模型:
The AC model consists of several tasks that include normalization, reduction, severity/prioritization, attack detection, and prediction to present a viewpoint of network security situations.
一个合理的流程包括规范化->简化->严重性/优先级排序->攻击检测和预测
- 规范化: Aggregation and correlation of intrusion-detection alerts 就异构告警数据的格式化给出了IDMEF标准,Security event taxonomy mapping 则给出了IDEA标准,,其JSON格式如下:
1 | { |
- 告警简化:主要分为聚合和过滤。
- 聚合:
- 过滤:
- 严重性/优先级排序:
- 攻击预测:事实上已经在’‘有关预测’'部分说过了。
- 数据集:
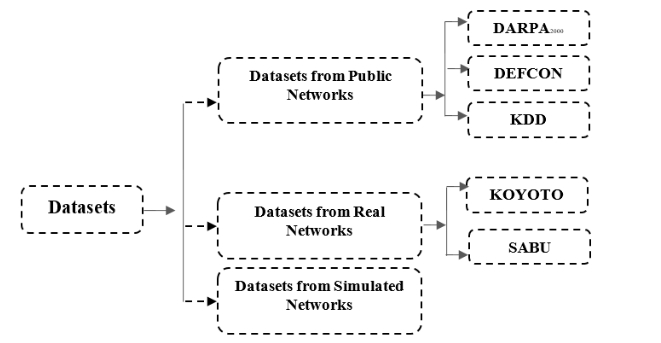
Summary:
标题也写着“告警关联技术”。从这里面找预测感觉也不那么靠谱。但是还是发现了几篇文章。
比较重要的是,对一般检测数据集,我们可能还需要进行一个合理的流程:规范化->简化->严重性/优先级排序->攻击检测和预测对告警进行处理。
第一篇在兴头上写的详细,后面会非常非常简单。
基于网络防御知识图谱的0day攻击路径预测方法
Year: 2022, Authors: 信息工程大学
Abstract:
针对 0day 漏洞未知性造成的攻击检测难问题,提出了一种基于知识图谱的 0day 攻击路径预测方法。通过从现有关于网络安全领域本体的研究成果及网络安全数据库中抽取“攻击”相关的概念及实体,构建网络防御知识图谱,将威胁、脆弱性、资产等离散的安全数据提炼为互相关联的安全知识。在此基础上,依托知识图谱整合的知识,假设并约束0day漏洞的存在性、可用性及危害性等未知属性,并将“攻击”这一概念建模为知识图谱中攻击者实体与设备实体间存在的一种关系,从而将攻击预测问题转化为知识图谱的链接预测问题。采用基于路径排序算法的知识图谱推理方法挖掘目标系统中可能发生的 0day 攻击,并生成 0day 攻击图。复用分类器输出的预测得分作为单步攻击发生概率,通过计算并比较不同攻击路径的发生概率,预测分析 0day 攻击路径。实验证明,所提方法能够依托知识图谱提供的知识体系,为攻击预测提供较全面的知识支持,降低预测分析对专家模型的依赖,并较好地克服 0day 漏洞未知性对预测分析造成的不利影响,提高了 0day 攻击预测的准确性,并且借助路径排序算法基于图结构这一显式特征进行推理的特点,能够对推理结果形成的原因进行有效反溯,从而一定限度上提高了攻击预测分析结果的可解释性。
Record:
一是条件假设缺乏有效约束,易导致 0day 攻击的预测结果规模过大,降低了预测的意义;
二是专家知识构建的攻击模型,易受专家主观知识面的制约;
三是在已知攻击路径不完整的情况下,预测方法难以适用。
文章为解决上述问题提出基于知识图谱的 0day 攻击路径预测方法,主体在于路径排序算法。
输入为网络防御知识图谱;关系路径集;
攻击样本集(历史攻击数据,用于训练分类器LCA,用以预测攻击是否会发生);0day攻击样本集(特定于0day攻击的数据样本,用于训练分类器LCZ,区分已知攻击和0day攻击)。
预测目标为可能发生的单步攻击,例如 (Firewall_1, 0day-001) 发生的可能性,然后根据资产间的权限关系矩阵,利用所有的单步攻击形成攻击路径。
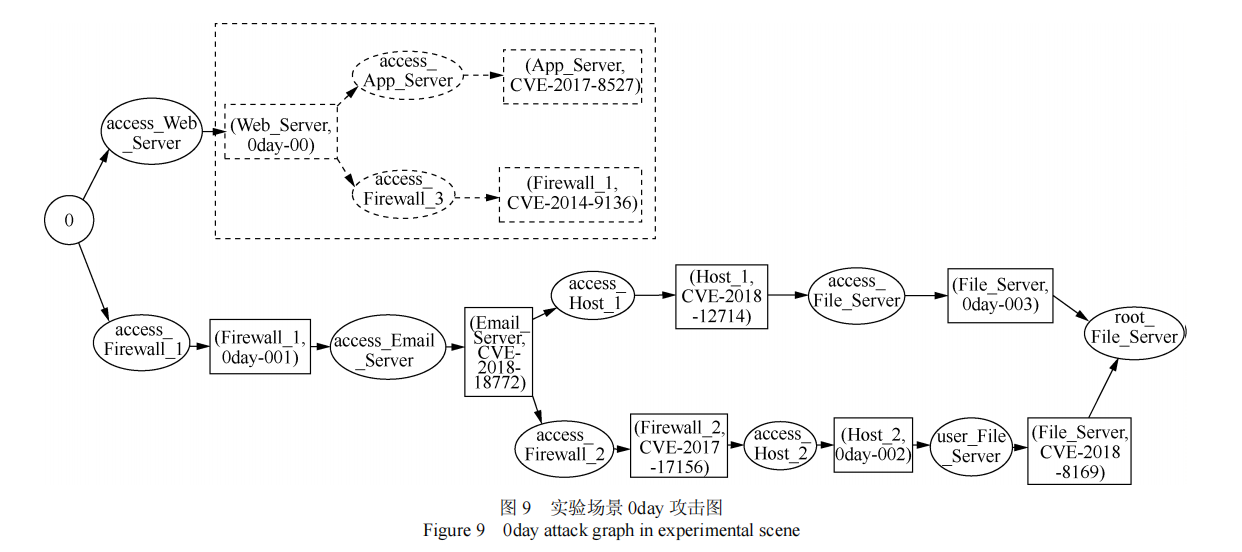
- 如何处理未知的0days攻击?
选取可用且能满足攻击者对相应设备攻击意图的技术漏洞模拟攻击者掌握的 0day 漏洞。例如,以代码执行漏洞 CVE-2020-14841 模拟 App_Server 的 weblogic_server 组件存在的 0day 漏洞,该漏洞仅需远程访问权限即可触发,获取权限越高,越容易触发,符合 0day 漏洞可用性假设,且执行后能够完成目标设备的控制,从而满足攻击者对 App_Server 的攻击意图。
简单来说就是找一个接近的CVE。
文章自己搭建实验所需的互联网环境,构建知识图谱,威胁、资产、脆弱性 3 个知识模块分别以信息工程大学 CTF 战队模拟的黑客组织、实验环境设备、不同场景中存在的脆弱性为核心构建相应实体。
以模拟攻击者的 CTF 战队对不同训练场景下的目标系统的攻击数据为基础,依托知识图谱,以其中被攻击成功的设备为目标实体,计算路径特征,构建攻击正样本,以攻击失败及未被选择为攻击目标的设备为目标实体,构建攻击负样本。
CyberSecurity Attack Prediction: A Deep Learning Approach
Abstract:
Cybersecurity attacks are exponentially increasing, making existing detection mechanisms insufficient and enhancing the necessity to design more relevant prediction models and approaches. This issue is still an open research problem since existing attack prediction models are failing to follow the huge amount of attacks and their variety. Recently, machine learning approaches and especially deep learning techniques have received much attention from researchers since their unparalleled high performance in several predictionbased fields. In this context, this paper explores the application of deep learning techniques for predicting cybersecurity attacks. Particularly, it proposes a new LSTM (Long Short-Term Memory), RNN (Recurrent Neural Network), and MLP (Multilayer Perceptron) based models carefully designed to predict the type of attack potentially to hap-pen. The proposed models were validated using a recently available dataset called CTF showing encouraging results especially for the LSTM model with an f-measure greater than 93%
Record:
基于一个简单的模型架构(LSTM/RNN+Dropout+全连接),作者给出了两种模型:
基本模型(Basic Model)的输入仅包含攻击发生时的IP源和IP目的地。
回顾模型(Looking Back Model)的输入除了IP源和IP目的地外,还加入了前一次攻击的类型(Attack Type_(t-1))作为额外输入。
模型的目标输出都是预测下一个时间点上发生的攻击类型。在实验中,使用了一个包含36种不同攻击类型的分类任务。
使用了被称为Ctf17数据集,由Defcon提供。Defcon是全球最大的互联网安全社区。Defcon提供了"夺旗" ( Capture the Flag,CtF )大赛,这是一场计算机安全攻防技能的较量。保卫自己的旗帜,同时要想方设法败坏其他球队的旗帜。标志是团队服务器上的数据文件。在博弈过程中,攻击者试图将别人服务器上的旗帜替换为自己的旗帜,而防御者则试图将自己的旗帜保留在自己的服务器上。可以在这里 找到历届比赛的内容,ctf17的可下载内容包含两个文件:DEF CON 17 Hacking Conference CTF - BinJitsu - Capture the Flag complete packet capture.rar 和 DEF CON 17 Hacking Conference - CTF Binaries.zip
将数据集传入Snort分析得到警报,除此之外没有更详细的数据处理过程。等待下载完毕后会进一步完善说明。
Predictive Methods in Cyber Defense: Current Experience and Research Challenges
Abstract:
Predictive analysis allows next-generation cyber defense that is more proactive than current approaches based on intrusion
detection. In this paper, we discuss various aspects of predictive methods in cyber defense and illustrate them on three
examples of recent approaches. The first approach uses data mining to extract frequent attack scenarios and uses them to
project ongoing cyberattacks. The second approach uses a dynamic network entity reputation score to predict malicious
actors. The third approach uses time series analysis to forecast attack rates in the network. This paper presents a unique
evaluation of the three distinct methods in a common environment of an intrusion detection alert sharing platform, which
allows for a comparison of the approaches and illustrates the capabilities of predictive analysis for current and future
research and cybersecurity operations. Our experiments show that all three methods achieved a sufficient technology
readiness level for experimental deployment in an operational setting with promising accuracy and usability. Namely
prediction and projection methods, despite their differences, are highly usable for predictive blacklisting, the first provides
a more detailed output, and the second is more extensible. Network security situation forecasting is lightweight and
displays very high accuracy, but does not provide details on predicted events.
Record:
提出了三种基本方法:
- 基于数据挖掘的攻击场景提取(attack projection):
该方法通过数据挖掘提取常见的攻击序列,并使用这些序列来预测未来的恶意行为。具体步骤包括数据预处理、输入清洗、警报过滤、警报聚合、数据挖掘、数据库构建和规则匹配(预测)。
- 需要的五元组为(源IP,传感器,类别,目的端口,时间戳)
- 警报聚合:重复警报的聚合、持续事件的聚合。
重复条目,即在发送和共享过程中出现的多份相同警报,可能是由于错误导致的。如果多个警报共享相同的键元素(上述的5元组以及目的IP地址),则只接受其中一个,其余的被忽略。
持续事件导致无状态入侵检测系统多次报告同一事件,每次都有不同的时间戳。例如,如果网络扫描需要一个小时,且扫描检测方法基于过去五分钟内数据包数量的阈值,那么检测系统会针对同一事件发出十二个警报,每个警报都有不同的时间戳。在这种情况下,只处理第一个警报,其余的被忽略。如果将所有这些警报都包含在数据挖掘中,会产生描述持续事件的序列,而在这种用例中这些序列是无用的。 - 数据挖掘:构建顺序数据库、执行数据挖掘算法。
顺序数据库中填充了从警报中得出的具有相同源IP地址的项集序列。项集是从警报中得出的没有源IP地址和时间戳的n元组 (sensor, category, dstport) 。通过共同的源IP地址对项集进行分组,并存储在顺序数据库中。对于在多个警报中出现的每一个唯一IP地址,一系列项集被插入到数据库中,并按时间戳排序。
选择了最适合给定用例的Top-K序列规则挖掘方法。该实现使用SPMF库中实现的算法,其中 K=10 。该方法选择从序列数据库中的序列派生的十个最频繁的序列规则。序列规则由两个项目集n元组和相应的支持度(s)和置信度(c)值组成。
2推1。
-
动态网络实体评分(attack predication):
该方法使用梯度提升决策树(GBDT)模型来估计每个IP地址在未来一段时间内发动攻击的概率。输入特征包括历史警报数据、地理位置信息和公共黑名单信息等。
它不预测即将发生的确切攻击;相反,它估计每个IP地址(或者可能是另一种类型的网络标识符,一个实体)在近期时间窗口(例如,接下来的24小时)内发起攻击的概率。
目标是估计每个来源(IP地址)在未来24小时内观察到特定类型警报的概率。 -
基于时间序列分析的网络攻击率预测(Network security situation forecasting):
该方法使用时间序列分析方法来预测未来一段时间内的安全警报数量。使用了多种时间序列预测模型,包括ARIMA模型、指数平滑模型(状态空间模型)、朴素方法和它们的组合。
实验在一个共同的入侵检测警报共享平台SABU上进行,该平台由捷克国家研究和教育网络(NREN)运营。使用SABU平台从2019年3月11日至3月17日收集的一周内的入侵检测警报数据。数据来自34个入侵检测系统、蜜罐和其他数据源。
数据集来源:Dataset of intrusion detection alerts from a sharing platform
Predictive Cyber Situational Awareness and Personalized Blacklisting: A Sequential Rule Mining Approach
Abstract:
Cybersecurity adopts data mining for its ability to extract concealed and indistinct patterns in the data, such
as for the needs of alert correlation. Inferring common attack patterns and rules from the alerts helps in under-
standing the threat landscape for the defenders and allows for the realization of cyber situational awareness,
including the projection of ongoing attacks. In this article, we explore the use of data mining, namely se-
quential rule mining, in the analysis of intrusion detection alerts. We employed a dataset of 12 million alerts
from 34 intrusion detection systems in 3 organizations gathered in an alert sharing platform, and processed
it using our analytical framework. We execute the mining of sequential rules that we use to predict security
events, which we utilize to create a predictive blacklist. Thus, the recipients of the data from the sharing
platform will receive only a small number of alerts of events that are likely to occur instead of a large number
of alerts of past events. The predictive blacklist has the size of only 3% of the raw data, and more than 60% of
its entries are shown to be successful in performing accurate predictions in operational, real-world settings.
Record:
主要是记录一下一个很重要的表格:
预测网络攻击是一个新兴的研究主题,通常以警报关联为基础。在此,我们总结了使用数据挖掘产生输出(如攻击模型和预测规则)的工作,这些输出可用于进行预测。Li等人和Lei等人。
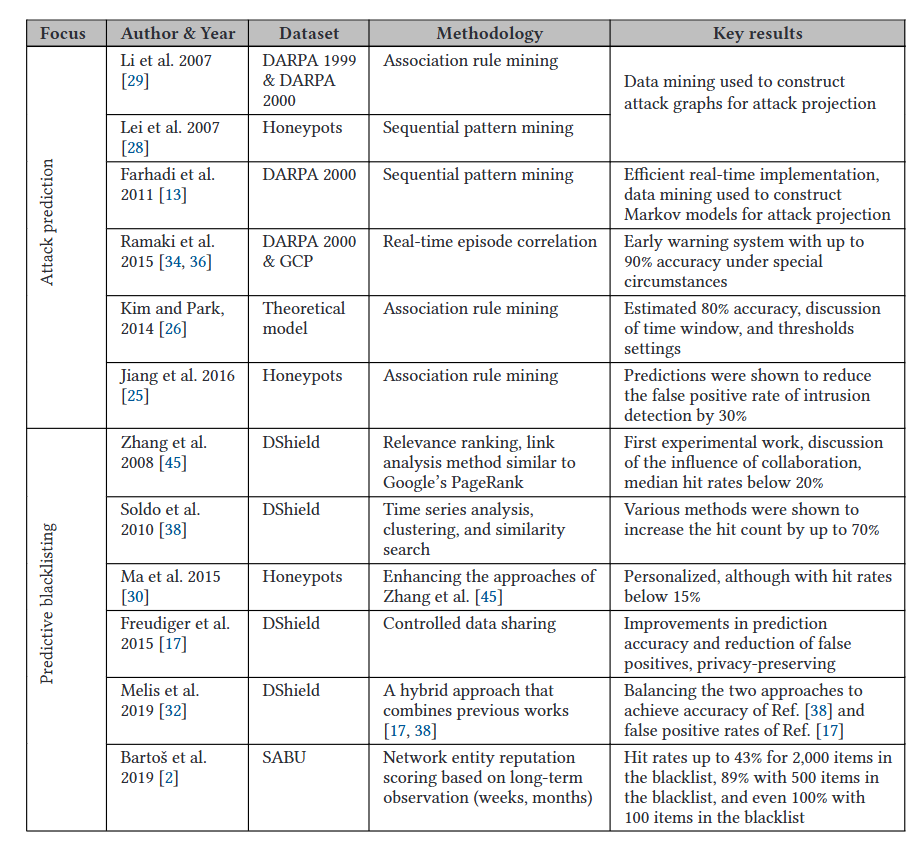
该表单统计了两种预测任务,分别是攻击预测和黑名单;黑名单旨在创建可能会表现出恶意行为的网络实体列表作为黑名单(例如IP地址和主机名)。
用的数据生成方案同Predictive Methods in Cyber Defense: Current Experience and Research Challenges
ProAPT: Projection of APT Threats with Deep Reinforcement Learning
Abstract:
The highest level in Endsley’s situation awareness model is called projection, when the status of elements in the
environment in the near future is predicted. In cybersecurity situation awareness, the projection for an Advanced
Persistent Threat (APT) requires to predict the next step of the APT.
The threats are constantly changing and becoming more complex. As supervised and unsupervised learning methods require APT datasets for projecting the next step of APTs, they are unable to identify unknown APT threats. In reinforcement learning methods, the agent interacts with the environment, and so it might project the next step of known and unknown APTs. So far, reinforcement learning has not been used to project the next step of APTs. In reinforcement learning, the agent uses the previous states and actions to approximate the best action of the current state. When the number of states and actions is abundant, the agent employs neural network which is called deep
learning to approximate the best action of each state.
In this paper, we present a deep reinforcement learning system to project the next step of APTs. As there exists some relation between attack steps, we employ Long- Short Term Memory (LSTM) method to approximate the best action of each state. In our proposed system, based on the current situation, we project the next steps of APT threats.
We have evaluated our proposed deep reinforcement learning system on the DAPT2020 dataset. Based on the evaluations performed on the mentioned dataset, six criteria F1, Accuracy, Precision, Recall, Loss, and average time were obtained, which are 0.9533, 0.9736, 0.9352, 0.97, 0.0143, and 0.05749(seconds) respectively. Although there
is no previous research on using reinforcement learning for APT projection, our results compared to the previous supervised and unsupervised methods proposed for multi-step attack projections indicate appropriate functioning.
Record:
方法为深度学习+强化学习。在强化学习(本文是Q学习)中,智能体通过与环境的交互来学习选择最优动作。当状态和动作的数量非常丰富时,智能体会使用神经网络(如LSTM)来近似每个状态的最优动作。其整体系统如下图所示:
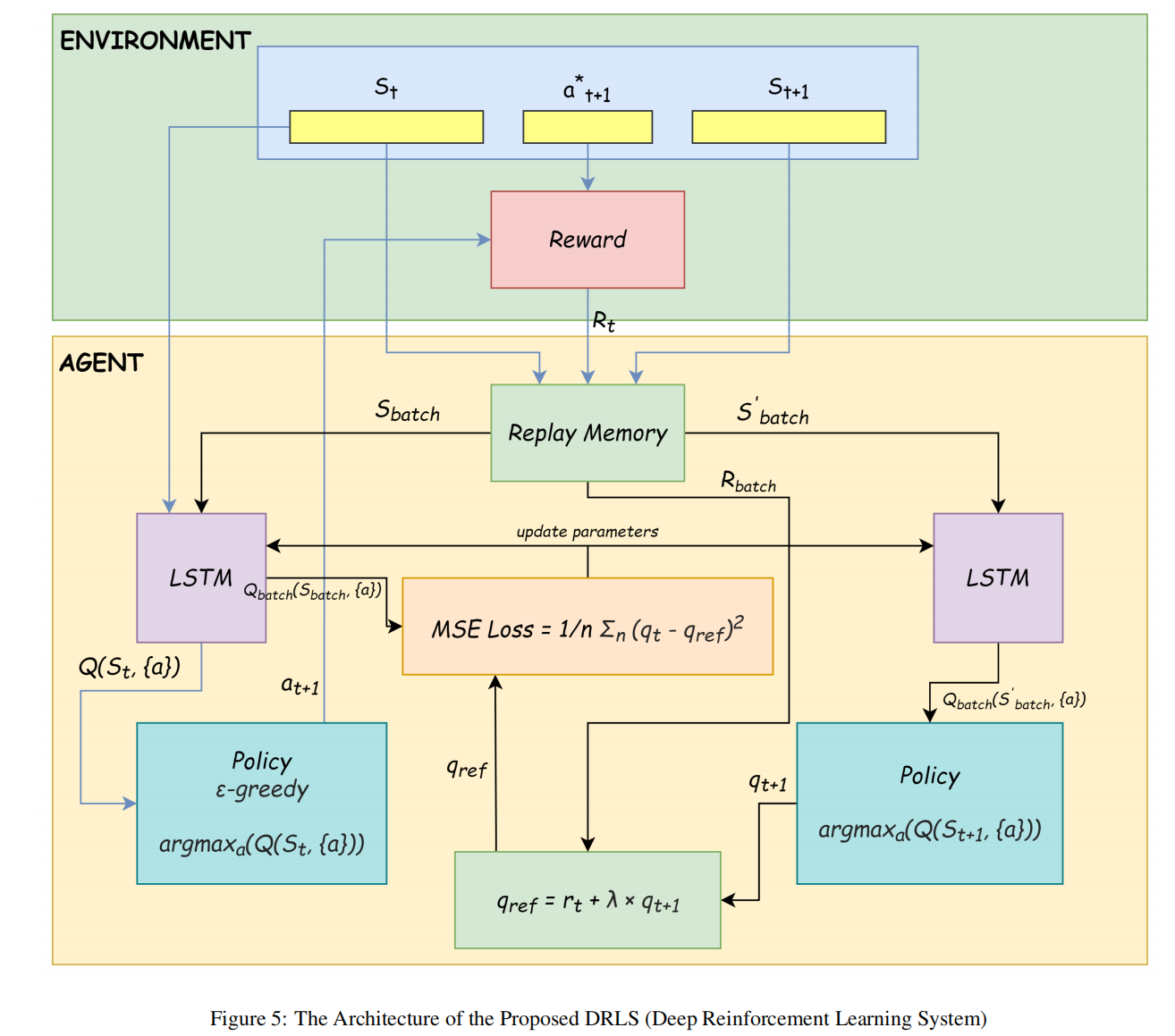
通过一些特征(如源IP地址、目的IP地址、源端口号、目的端口号、时间戳、攻击类型等)来展示每个状态(St)。代理接收当前状态,并根据贪心策略选择最佳行动。实际上,代理接收相关警报并选择下一步攻击。奖励是对正确/错误攻击预测的1/0。我们使用Q学习算法来训练代理。为了近似Q函数,我们采用LSTM,因为攻击步骤之间存在一些关系。Q函数提供了在特定状态和动作下的最大预期奖励。
输入是源IP地址、目的IP地址、源端口号、目的端口号、时间戳、攻击类型等形成的特征,希望预测下一步的攻击标签(任务和CL-AP2差不多,方法上有很大差别)
数据集可以直接在kaggle dapt2020下载,17G;文章本身的任务定义是下一步的APT类别预测,这不是期望得到的,但这个数据集可获取并且有较多的特征,所以记录下来,原始的论文为 DAPT 2020 - Constructing a Benchmark Dataset for Advanced Persistent Threats 。
这个数据集和其他所有攻击预测论文使用的数据集一样,其初衷仍然是攻击检测,而非攻击预测。
Survey of Attack Projection, Prediction, and Forecasting in Cyber Security
Abstract:
This paper provides a survey of prediction, and forecasting methods used in cyber security. Four main tasks are discussed first, attack projection and intention recognition, in which there is a need to predict the next move or the intentions of the attacker, intrusion prediction, in which there is a need to predict upcoming cyber attacks, and network security situation forecasting, in which we project cybersecurity situation in the whole network. Methods and approaches for addressing these tasks often share the theoretical background and are often complementary. In this survey, both methods based on discrete models, such as attack graphs, Bayesian networks, and Markov models, and continuous models, such as time series and grey models, are surveyed, compared, and contrasted. We further discuss machine learning and data mining approaches, that have gained a lot of attention recently and appears promising for such a constantly changing environment, which is cyber security. The survey also focuses on the practical usability of the methods and problems related to their evaluation.
Record:
论文中提到:
Yang et al. formalized the task of attack projection and surveyed literature on the topic in 2014. Three categories are listed, prediction based on attack plans, estimates of attackers capabilities and intentions, and predictions by learning attack patterns and attacker’s behavior.
Yang这里这篇文章就叫Attack Projection,其对攻击的分类与我在 《网络空间安全防御与态势感知》 阅读到的一致。而该综述的作者融合了后来的几种分类方法,给出了自己的分类方案:
| Use case | Task description | Previous surveys |
|---|---|---|
| Attack projection | What is an adversary going to do next? | Attack Projection |
| Attack intention–recognition | What is an ultimate goal of an adversary? | Attack intention recognition: A review, |
| Attack / Intrusion prediction | What type of attack will occur, when, and where? | Intrusion Prediction Systems |
| Network security situation forecasting | How is the overall situation going to evolve? | Network Security Situation Prediction: A Review and Discussion. |
作者简单说明了这几种方法预期的输出:
历史上,首批此类用例是攻击预测和攻击意图识别,这两者与入侵检测密切相关。任务是预测一个已观察到的攻击中的攻击者接下来会做什么,以及攻击者的最终目标是什么。
后来,出现了预测攻击的任务。这项任务更为通用,因为它不需要观察先前的活动。预期结果是在攻击实际发生之前对攻击进行预测,而不是预测观察到的连续事件序列的延续。
最后,预测安全状况的任务是与网络情境感知高度相关的通用用例。任务不是预测攻击,而是预测整个网络中的情况。结果可能是预测网络中攻击或漏洞数量的增加或减少。
实际上这样看下来,攻击预测和攻击意图识别比较靠近我期望的预测结果,那么意图识别和攻击预测有什么区别?
区别在于动机。在攻击预测中,我们并不太关心攻击者的意图。如果估计了对手的最终目标,对未来恶意事件的预测可能更适合特定的攻击。攻击者意图识别在网络取证中进行研究,最初是基于历史数据进行的。
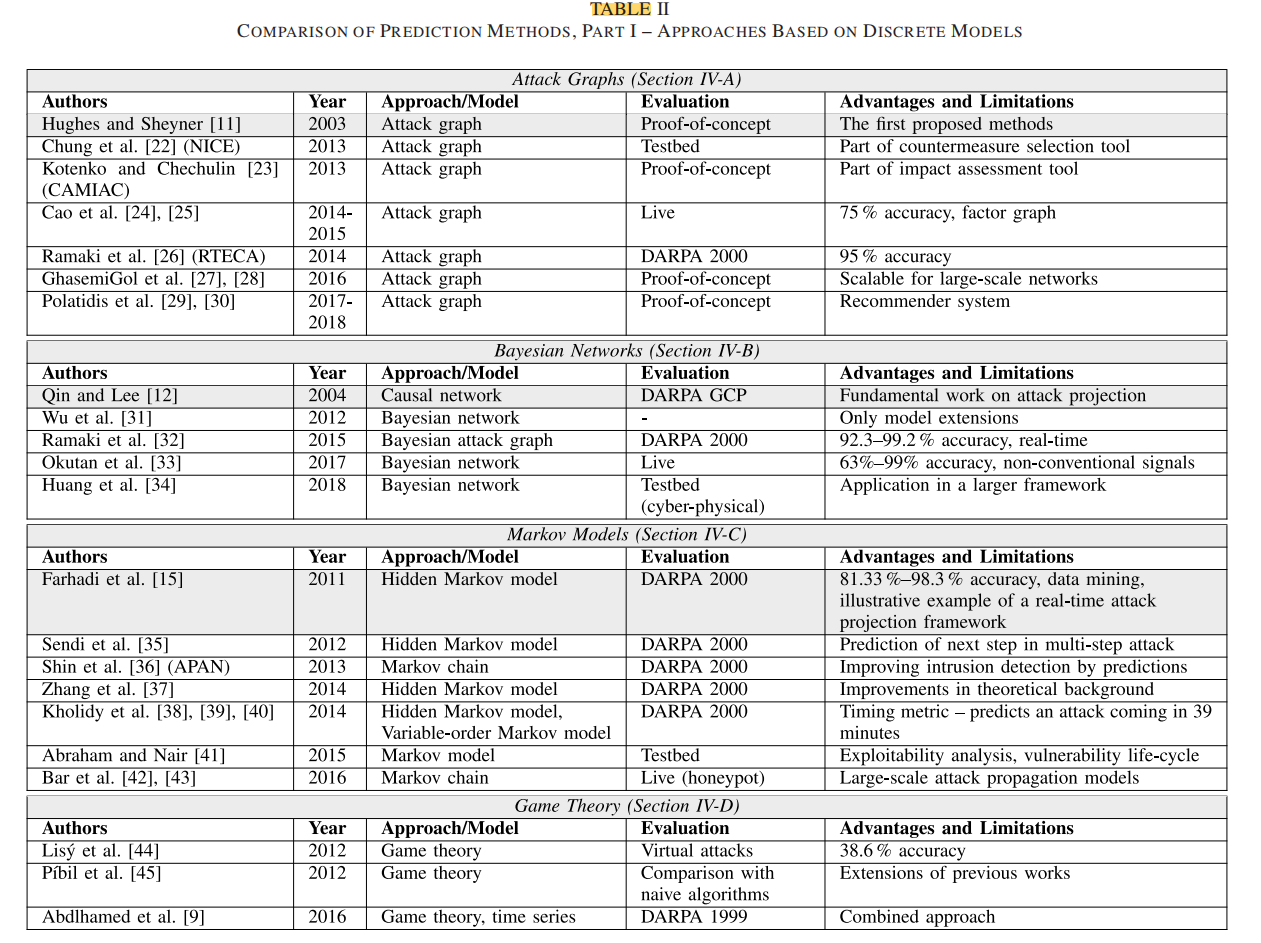
最重要的地方在于,文章对几种攻击预测的方法做了详细的统计:
- 图模型(离散模型)的方法,如攻击图、贝叶斯网络和马尔可夫模型。另一种替代方法是基于博弈论:
- 连续模型,如时间序列和灰色模型。这些方法在大多数情况下适用于网络安全状况的预测。常见的结果包括网络受到的攻击数量、攻击量和组成以及它们在时间上的分布。或者,可以使用时间序列中的时间模式来预测网络攻击:
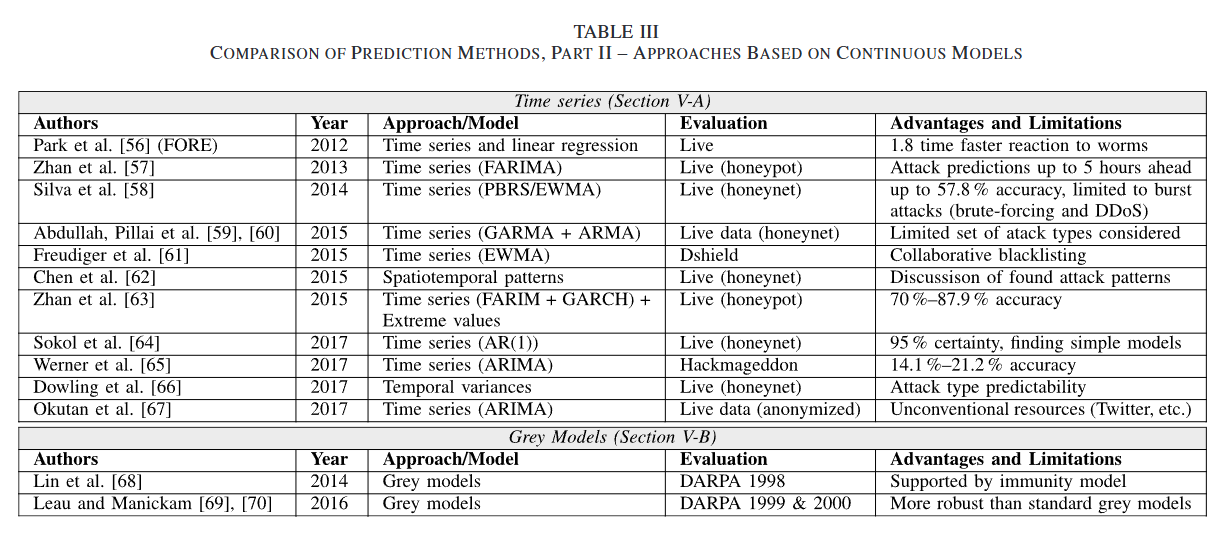
- 通常,数据挖掘被用于创建用于攻击预测的模型,例如,攻击图和马尔可夫模型。在此背景下使用数据挖掘的目的是为了克服基于模型的攻击预测模型的一个主要缺点,即依赖于安全专家提供的模型,并不直接影响方法本身。
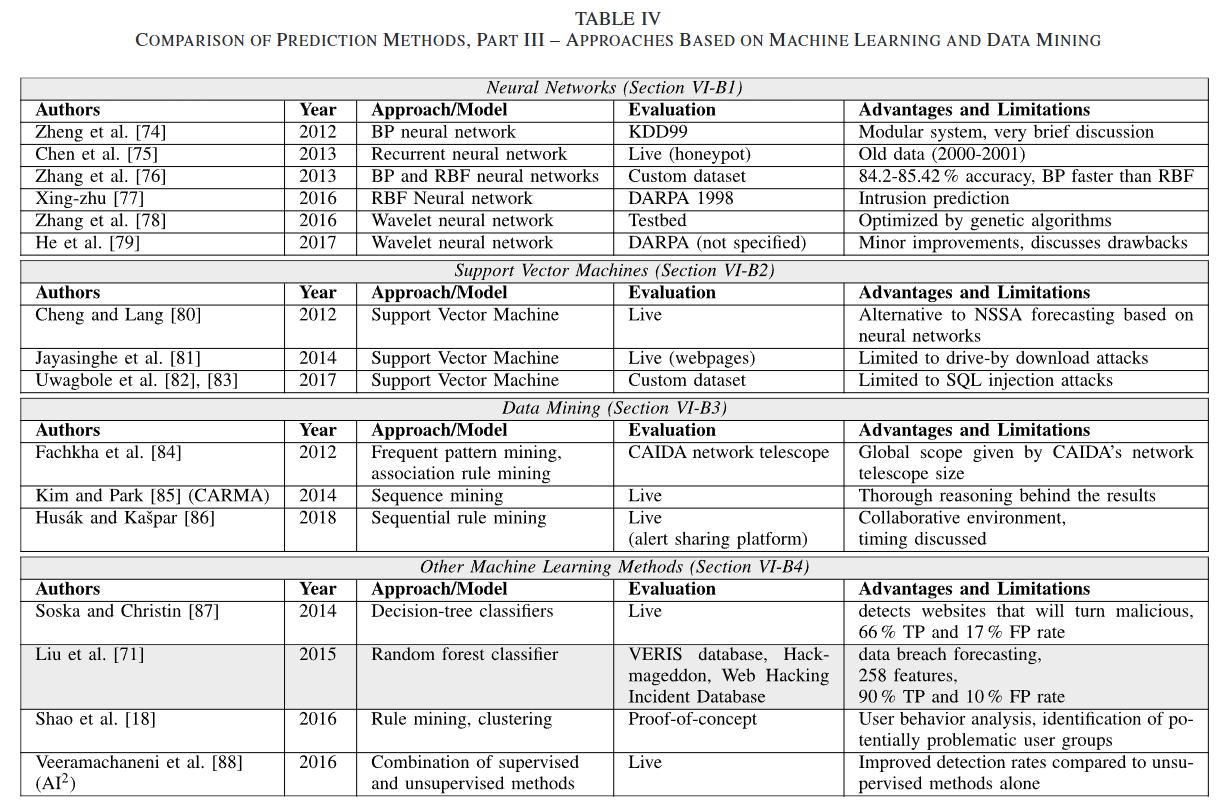
- 其他
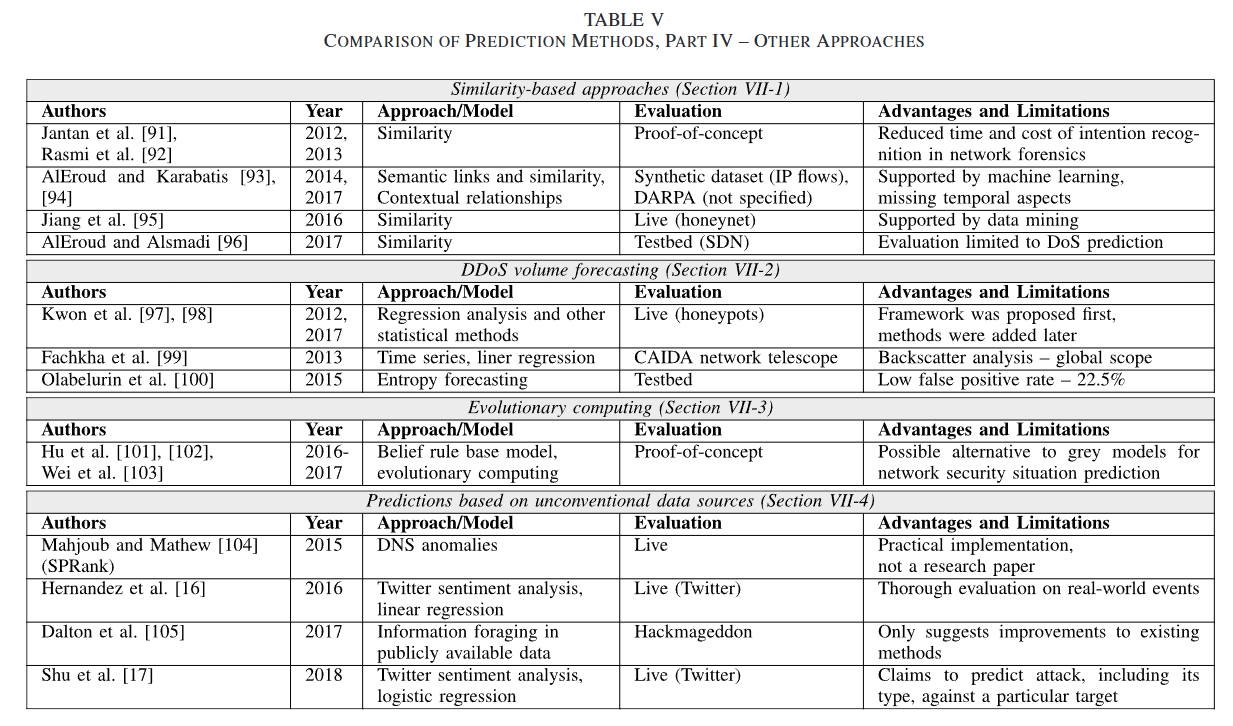
文章为表格中的所有工作都撰写了简单的总结,其中部分工作具有参考意义,集中在离散模型部分:
- 攻击图:攻击图(通常简称为AG)是一个元组 $G=(S, r, S_0, S_s)$,其中S是一组状态,$r⊆S×S$ 是一个转移关系(带概率),$S_0$是一个初始状态的集合,$S_s$是一个成功状态的集合。状态代表攻击开始前的状态,关系代表攻击者的可能行动。(有点像博弈论的决策树过程)
下图描述了一系列的攻击步骤,从ICMP PING开始进行目标探测,到尝试通过Telnet获取信息、利用RPC服务中的漏洞尝试获取root权限等,直至最终可能的攻击响应和进一步的恶意行为。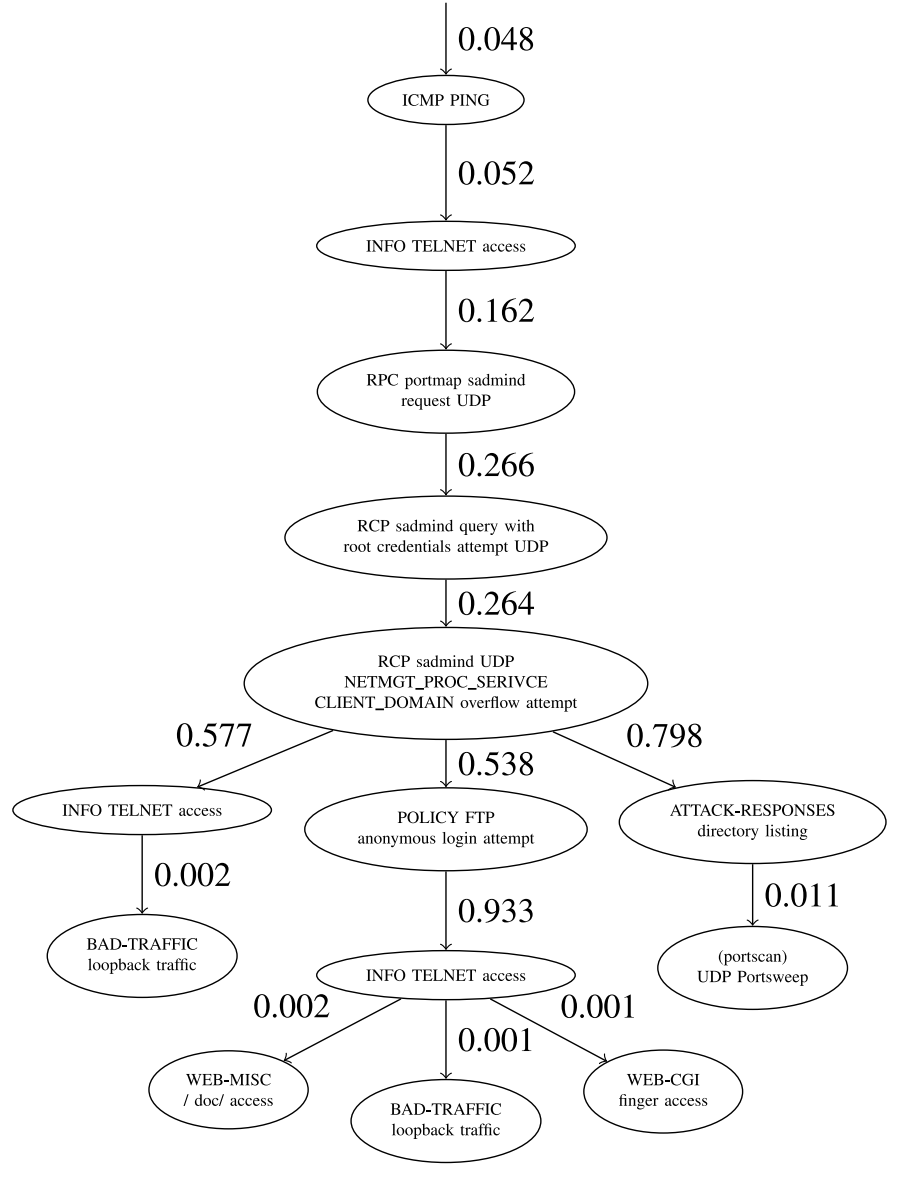 状态如何定义?
状态如何定义?
怎么构建?(详情见论文 A data mining approach to generating network attack graph for intrusion prediction)
怎么预测? - 贝叶斯网络:这些方法与基于攻击图的模型检验方法密切相关,因为贝叶斯网络通常是从攻击图中构建的。(对事件因果性的要求导致使用因果网络而不是通用的贝叶斯网络),
下图模拟了一个攻击者(D)的活动,该攻击者可能会使用缓冲区溢出漏洞利用(B、C)之一来获取对服务器(A)的访问权限。概率表附加在每个节点上,告知我们有关攻击者可能使用的漏洞利用的概率,以及成功利用的概率。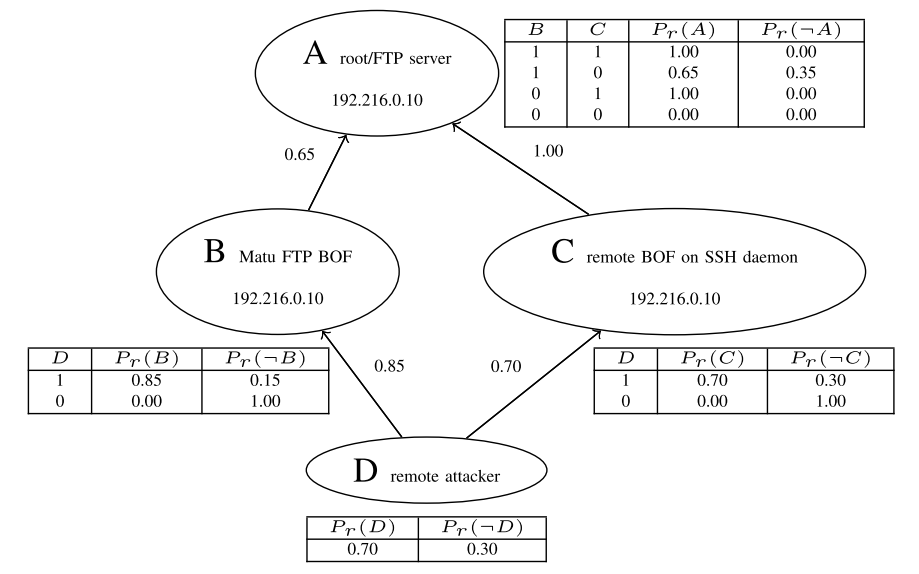
- 马尔可夫模型:
A Data Mining Approach to Generating Network Attack Graph for Intrusion Prediction
Abstract:
A network attack graph provides a global view of all possible sequences of exploits which an intruder may use to penetrate a system. Attack graphs can be generated by model checking techniques or intrusion alert correlation. In this paper we proposed a data mining approach to generating attack graphs. Through association rule mining, the algorithm generates multi-step attack patterns from historical intrusion alerts which comprise the attack graphs. The algorithm also calculates the predictability of each attack scenario in the attack graph which represents the probability for the corresponding attack scenario to be the precursor of future attacks. Then the real-time intrusion alerts can be correlated to attack scenarios and ranked by the predictability scores. The ranking result can help identify the appropriate evidence for intrusion prediction from a large volume of raw intrusion alerts. The approach is validated by DARPA 2000 and DARPA 1999 intrusion detection evaluation datasets.
Record:
关联规则的方法,$[x,y] \rightarrow z$,由历史入侵检测系统(IDS)警报构成的数据集,在处理之前需要经过一些预处理功能,比如提高数据集质量的警报聚合和警报验证,映射警报属性以便于计算,以及使用滑动攻击序列时间窗口划分全局警报序列。统计每一种攻击序列出现的频数,按支持度大小赋予状态间的转移概率。
Using Attack Graphs for Correlating, Hypothesizing, and Predicting Intrusion Alerts
Abstract:
To defend against multi-step intrusions in high-speed networks, efficient algorithms are needed to correlate isolated alerts into attack scenarios. Existing correlation methods usually employ an in-memory index for fast searches among received alerts. With finite memory, the index can only be built on a limited number of alerts inside a sliding window. Knowing this fact, an attacker can prevent two attack steps from both falling into the sliding window by either passively delaying the second step or actively injecting bogus alerts between the two steps. In either case, the correlation effort is defeated. In this paper, we first address the above issue with a novel queue graph (QG) approach. Instead of searching all the received alerts for those that prepare for a new alert, we only search for the latest alert of each type. The correlation between the new alert and other alerts is implicitly represented using the temporal order between alerts. Consequently, our approach can correlate alerts that are arbitrarily far away, and it has a linear (in the number of alert types) time complexity and quadratic memory requirement. Then, we extend the basic QG approach to a unified method to hypothesize missing alerts and to predict future alerts. Finally, we propose a compact representation for the result of alert correlation. Empirical results show that our method can fulfill correlation tasks faster than an IDS can report alerts. Hence, the method is a promising solution for administrators to monitor and predict the progress of intrusions and thus to take appropriate countermeasures in a timely manner.
Record:
攻击图的开山论文。
最初攻击图的设想来自告警关联——警报可以根据相似属性(例如,相同的目的主机)以及关于警报类型或相应漏洞的先验知识进行关联。
提出了一种新颖的队列图方法、一种统一的入侵警报关联、假设和预测方法。
- 攻击图:攻击图代表了对给定网络的先验知识,以漏洞和连通性为基础。攻击图是一种有向图,两种顶点:利用、安全条件。利用是指绑定于主机的漏洞,被表示为一个三元组(漏洞,源主机,目标主机),表明漏洞存在于目标主机上,并且源主机和目标主机是连接的(源主机和目标主机可能在本地利用中指的是同一台主机)。安全条件是指利用漏洞所需或暗示的网络状态,如权限级别或信任。两种有向边:安全条件->利用漏洞,表示只有当满足安全条件时才能执行该利用;利用漏洞->安全条件,表示执行该利用将满足安全条件。示例如下(椭圆为安全条件、矩形为利用):
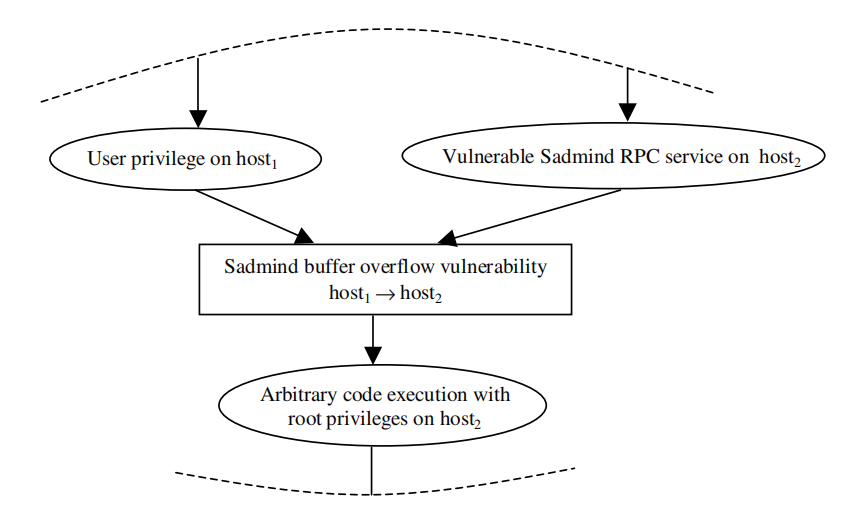 只有在攻击者能够访问源主机host1且目标主机host2存在易受攻击的服务时,缓冲区溢出利用才能执行
只有在攻击者能够访问源主机host1且目标主机host2存在易受攻击的服务时,缓冲区溢出利用才能执行 - 入侵警报:由给定网络中的IDS传感器报告的入侵警报通常包含事件类型、源主机和目的主机的地址、时间戳等属性(RPC端口映射sadmind请求UDP,202.77.162.213,172.16.115.20,03/07-08:50:04.74612)。
现在说明了原始数据结构和攻击图,暂且跳过具体的队列图关联过程,只看在攻击预测的应用:
通过向后搜索(即,沿着攻击图中边的相反方向)来查找相关(或假设)的警报,可以解释新警报的出现(溯源图?)。通过向前搜索来预测每个新警报的可能后果。在这种情况下使用BFS,预测出的安全条件将按照它们到新警报的(最短)距离顺序被发现。这个距离大致表明了基于迄今为止收到的警报,预测攻击的紧迫程度。(实际上是预测下一步攻击的结果,或者安全条件映射到攻击?)
很明显的,这种方法无法预测未知攻击。当观测到某一步告警(即攻击图中的利用)出现,在已有构建好的攻击图基础上,查看该利用的后续安全条件(即攻击图中的安全条件)以得到可能的攻击。与CyberSecurity Attack Prediction: A Deep Learning Approach方法不同,现实世界不可能得到完整的攻击图——攻击一直在变化,最多给出1、已知攻击的先验(MITRE)2、已经检测到了发生的攻击。3、系统日志(告警)4、系统的物理环境组成。
实验部分,使用了两个数据集进行实验,一个是麻省理工学院林肯实验室的DARPA2000入侵检测LLDOS 1.0,另一个是University of California, Santa Barbara的寻宝活动数据集(互联网好像已经找不到了,也没看到有人用)。Darpa 2000数据集中的攻击场景之前已经被广泛探索过(见Constructing attack scenarios through correlation of intrusion alerts)。
Reference
感觉也没什么必要写,出现的文章都有名字。